copied
copied copied
copiedhex = "ab"
binary = [hex].pack("H*") # H = hex string (highest byte first), * = multiple bytesHash Function
Fingerprints for data
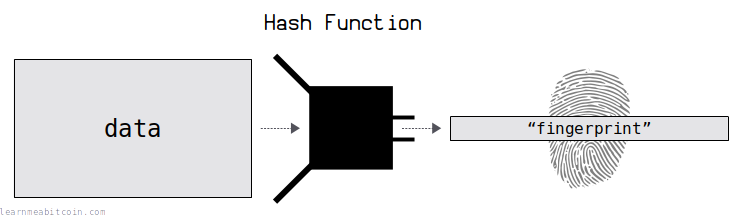
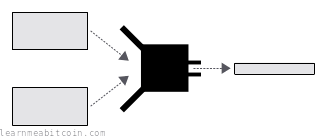
A hash function is a programming tool that creates fingerprints for data.
It takes in any amount of data, scrambles it, and returns a short and unique result for that data.
SHA = Secure Hashing Algorithm, 256 = 256 bits (the size of the hash result).
The result of the hash function is just a bunch of bytes. So the letters and numbers you're seeing are just bytes of data represented by hexadecimal characters, which is typically how the outputs of hash functions are displayed.
Technical terms
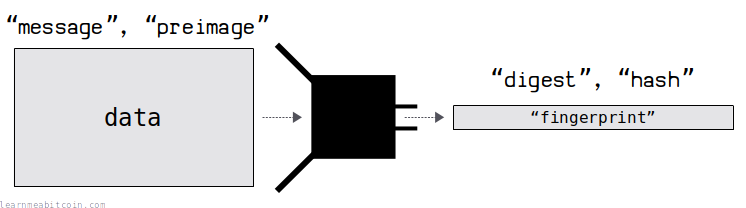
Here are some technical terms that crop up from time to time:
- The data you insert into the hash function is referred to as the "message" or "preimage".
- The result of the hash function is sometimes referred to as the "digest" or simply the "hash".
"Preimage" is probably the most awkward technical term you'll come across, but it just refers to some specific data you insert into the hash function.
I prefer to use the terms "data" and "hash", but don't be surprised if you run into the other terms now and then.
Properties
What makes a hash function a hash function?
There are a few different properties that separate a basic hash function from a strong hash function
Basic Hash Function
There are a few basic properties of hash functions that you've probably already noticed:
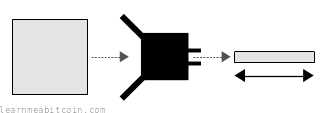
- You always get the same result for the same data. If you and someone else insert the same data into the same hash function, you'll both get the same result. This is known as being deterministic.
- You get a fixed-length result no matter the size of the data. A hash function can take in any amount of data, and it will scramble and compress it to produce a (usually) shorter result. The size of the hash varies between hash functions, but for SHA-256 it's 256 bits (32 bytes) in size.
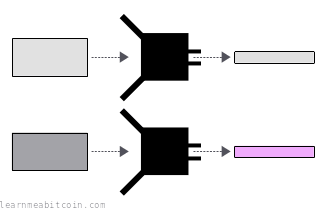
- You get wildly different results with small changes to the data. What comes out of the hash function appears to be random. Even the smallest change to the data you insert to the hash function will produce completely different results. This is known as the avalanche effect.
Those are the obvious features you'd expect from a good "fingerprinting machine".
Strong Hash Function
(aka Cryptographic Hash Function)
There are some properties of strong hash functions (e.g. SHA-256) that you may not have noticed:
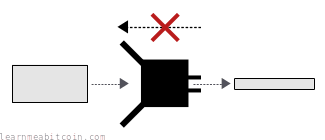
- A strong hash function is irreversible. If I gave you a hash result, you wouldn't be able to work out the original data that I used to create it. The only way you could hope to find it would be to try different inputs in a brute-force search, which would be computationally infeasible given the massive range of possible outputs. Anyway, this property of not being able to work backwards is known as one-wayness.
- Every piece of data should have its own unique result. Obviously this is technically impossible as there are infinite combinations of data out there. However, a secure hash function should make it computationally infeasible to find two different pieces of data that produce the same hash digest. This property is known as collision resistance.
- You can't control the result of a strong hash function. There's no way you can figure out how to construct an input to give you a specific result from a hash function. If you want a specific result, you just have to keep hashing different pieces of data to get the kind of result you want. This property is known as preimage resistance.
A hash function is referred to as a "cryptographic hash function" if it achieves these 3 strong properties.
This means that it's usually slower than a basic hash function (although still pretty fast overall), but it also means it can be relied upon to be unpredictable and produce unique results for different pieces of data. Which is an important feature when it comes to cryptography.
So as you can guess, Bitcoin uses cryptographic hash functions:
Technical terms
This is just for my reference if nothing else, as I keep forgetting what each of these terms mean when reading about secure hash functions in textbooks.
Anyway, in technical terms, a "cryptographic hash function" should possess the 3 following key properties:
- Second Preimage Resistance (Weak Collision Resistance)
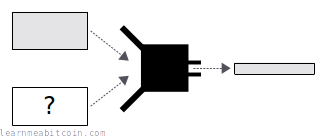
- Given some data and its hash result, it's hard to find another piece of data that will hash to the same result. This is occasionally referred to as weak collision resistance.
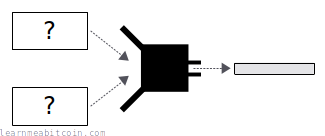
- Collision Resistance
- It's hard to find any two pieces of data that hash to the same result. This is similar to the last property, but whereas in second preimage resistance you are stuck with some starting data and have to find another piece of data that produces the same result, with collision resistance you are free to choose any two pieces of data that produce the same hash result. This is therefore sometimes referred to as strong collision resistance.
- These three terms seem to get mixed up from time to time (especially because second preimage resistance is a form of collision resistance).
- To put it another way, you have preimage resistance, and two types of collision resistance.
And what is a preimage exactly?
Preimage (mathematics) - The set of arguments of a function corresponding to a particular subset of the range.
So a "preimage" is something that you put into a function that maps to a specific result.
Bitcoin
What hash functions does Bitcoin use?
There are five methods for hashing data in Bitcoin:
- HASH256 – Double SHA-256 (most common)
- HASH160 – SHA-256 + RIPEMD-160
- SHA-256 – Single SHA-256
- HMAC-SHA512 – HMAC with SHA-512
- PBKDF2 – Password Based Key Derivation Function 2
In Bitcoin we hash bytes of data. So in the tools below, you need to represent bytes by using hexadecimal characters (where every byte is made from two hex characters). See a common mistake with hashing for more details.
HASH256
SHA-256(SHA-256(data))
If you're hashing something in Bitcoin, you're almost always using HASH256.
This works by putting the data through SHA-256, then taking the result and put it through SHA-256 again.
You may notice that the hashes you get for block data and transaction data appear to be backwards. This is because block hashes and transaction hashes are actually in reverse byte order when searching for them using bitcoin-cli and on blockchain explorers.
This is the primary method for hashing data in Bitcoin. It's sometimes referred to as "double-SHA256" or "SHA-256d", but in code it's most commonly called hash256 for short.
Here are some examples of where you'll find HASH256 being used in Bitcoin:
Code

 copied
copied copied
copiedrequire 'digest'
def hash256(hex)
# convert hexadecimal string to byte sequence first
binary = [hex].pack("H*") # H = hex string (highest byte first), * = multiple bytes
# SHA-256 (first round)
hash1 = Digest::SHA256.digest(binary)
# SHA-256 (second round)
hash2 = Digest::SHA256.digest(hash1)
# convert from byte sequence back to hexadecimal
hash256 = hash2.unpack("H*")[0]
return hash256
end
puts hash256("aa") #=> e51600d48d2f72eb428e78733e01fbd6081b349528335bf21269362edfae185d
Why do we hash twice?
Satoshi never mentioned why they chose double-SHA256 when designing Bitcoin.
Satoshi was probably concerned about something called a length extension attack, and it has been recommended in some literature (e.g. Cryptography Engineering) to use double-SHA256 to protect against it.
These kinds of attacks are not a concern for Bitcoin though, so either Satoshi was misguided in their choice of using double-SHA256, or they just wanted to be extra cautious.
Satoshi standardized on using double-SHA256 for 32-byte hashes, and SHA256+RIPEMD160 (each once) for 20-byte hashes, presumably because of (likely misguided) concern about certain attacks (like length extension attacks, which only apply when hashing secret data), and then used those everywhere.
Either way, hashing data twice is now just a quirk of Bitcoin.
If you designed Bitcoin from scratch today there would be no benefit to using double-SHA256. In fact, recent upgrades to Bitcoin now favor using single-SHA256 where possible (e.g. script hashes in P2WSH).
Hash160
RIPEMD-160(SHA-256(data))
HASH160 is used infrequently in Bitcoin.
This works by putting the data through SHA-256, then taking the result and put it through another hash function called RIPEMD-160.
HASH160 is only used when constructing legacy addresses:
Upgrades to Bitcoin over the years have not made further use of HASH160 when hashing data, and so now it's only used when constructing addresses for legacy locking scripts.
Code

 copied
copied copied
copiedrequire 'digest'
def hash160(data)
# convert hexadecimal string to byte sequence first
binary = [data].pack("H*") # H = hex string (highest byte first), * = multiple bytes
# SHA-256
sha256 = Digest::SHA256.digest(binary)
# RIPEMD-160
ripemd160 = Digest::RMD160.digest(sha256)
# convert from byte sequence back to hexadecimal
hash160 = ripemd160.unpack("H*").join
return hash160
end
puts hash160("aa") #=> 58d179ca6112752d00dc9b89ea4f55a585195e26
Why RIPEMD-160?
RIPEMD-160 produces a shorter digest than SHA-256:
| Hash Function | Digest Size | Example |
|---|---|---|
| SHA-256 | 32 bytes (256 bits) | e51600d48d2f72eb428e78733e01fbd6081b349528335bf21269362edfae185d |
| RIPEMD-160 | 20 bytes (160 bits) | 58d179ca6112752d00dc9b89ea4f55a585195e26 |
So RIPEMD-160 is ideal for creating shorter (yet still secure) fingerprints for public keys and scripts.
As for why Satoshi chose RIPEMD-160 over something like SHA-1 (which also produces 160-bit digests), I'm not sure. It could have been because RIPEMD-160 was known to be more collision resistant at the time (SHA-1 has had collisions since, so a wise choice in hindsight), or because Satoshi simply preferred to use a hash function designed by a separate organization.
Unlike all SHA-1 and SHA-2 algorithms, RIPEMD-160 is the only one that was not designed by NIST and NSA, but rather by a team of European researchers. Even though there is no indication that any of the SHA algorithms are artificially weakened or contain backdoors (introduced by the US government, that is), RIPEMD-160 might appeal to some people who heavily distrust governments.
It is worth noting that Satoshi could've used SHA2-256 twice and truncated the second digest to 160 bits as this is equally secure. The fact that he didn't is some evidence to show that his decision was a conscious decision to use RIPEMD-160 over the NSA suit of algorithms.
Either way, RIPEMD-160 is a fine choice for use as a 160-bit hash function, even if we don't really use it much any more in Bitcoin.
The use of SHA-256 + RIPEMD-160 helps to prevent against length extension attacks too (even though this is once again unnecessary).
SHA-256
SHA-256(data)
This is where you just the data through SHA-256 once. Nothing special this time.
This tool only accepts bytes of data in the form of hexadecimal characters. This is different to the SHA-256 (Text) tool at the top of the page, which accepts any text data, but that's just an example tool and is not the way data is hashed in Bitcoin.
More recent changes to Bitcoin have started to use a single round of SHA-256 (instead of HASH256):
However, it's nowhere near as prevalent as HASH256. So as a general rule, if you're hashing something in Bitcoin, it's most likely to be HASH256 and not a single SHA-256.
Code

 copied
copied copied
copiedrequire 'digest'
def sha256(hex)
# convert hexadecimal string to byte sequence first
binary = [hex].pack("H*") # H = hex string (highest byte first), * = multiple bytes
# SHA-256 (single)
hash = Digest::SHA256.digest(binary)
# convert from byte sequence back to hexadecimal
sha256 = hash.unpack("H*")[0]
return sha256
end
puts sha256("aa") #=> bceef655b5a034911f1c3718ce056531b45ef03b4c7b1f15629e867294011a7dHMAC-SHA512
HMAC with SHA-512
We use HMAC-SHA512 when we want to hash some data with an additional secret key.
- HMAC - The method for hashing some data with an additional key.
- SHA-512 - The hash algorithm used within the HMAC.
So SHA-512 is the actual hash algorithm, and HMAC (Hash-based Message Authentication Code) is the method for combining the two pieces of data together using that hash algorithm.
HMAC-SHA512 is used in Bitcoin when creating extended keys in HD Wallets:
SHA-512 is used within the HMAC when creating extended keys because it produces a 64 byte hash result, which means you can chop up the result to get a new private key (the first 32 bytes) and a new chain code (the last 32 bytes) to form the child extended key.
- In general cryptography, a HMAC is used when you want to hash some data, but also want to hash it with an additional secret key so that you can only get the same result if you have both the original data and the secret key.
- Using a HMAC protects against length-extension attacks, which means it's a safer method than simply appending the secret key to the data and hashing it that way.
Code

 copied
copied copied
copiedrequire 'openssl'
# Example data
data = "67f93560761e20617de26e0cb84f7234aaf373ed2e66295c3d7397e6d7ebe882ea396d5d293808b0defd7edd2babd4c091ad942e6a9351e6d075a29d4df872af"
key = "Bitcoin seed"
# HMAC-SHA512
hmac = OpenSSL::HMAC.hexdigest(OpenSSL::Digest::SHA512.new, key, [data].pack("H*"))
puts hmac #=> f79bb0d317b310b261a55a8ab393b4c8a1aba6fa4d08aef379caba502d5d67f9463223aac10fb13f291a1bc76bc26003d98da661cb76df61e750c139826dea8bPBKDF2
Password Based Key Derivation Function 2
PBKDF2 is used when you want to hash data multiple times.
The fact that PBKDF2 uses multiple iterations for hashing means that it is intentionally slow, which makes it more difficult to perform brute-force attacks.
So PBKDF2 is not actually a hash algorithm itself, but instead uses an existing hash algorithm (e.g. HMAC-SHA512) with multiple repetitions (in a specific way) before producing the final result.
In Bitcoin, PBKDF2 is used on the mnemonic sentence to create the initial seed for use in HD Wallets.
Bitcoin uses 2,048 iterations of PBKDF2 to convert a mnemonic sentence (and optional passphrase) to a seed. This makes it more time-consuming to try and crack someone else's mnemonic sentence and/or passphrase.
Code

 copied
copied copied
copiedrequire 'openssl'
# Example data
mnemonic = "punch shock entire north file identify"
passphrase = ""
# Prepare data for PBKDF2
password = mnemonic
salt = "mnemonic#{passphrase}" # "mnemonic" is always used in the salt with optional passphrase appended to it
iterations = 2048
keylength = 64
digest = OpenSSL::Digest::SHA512.new
# PBKDF2
result = OpenSSL::PKCS5.pbkdf2_hmac(password, salt, iterations, keylength, digest)
seed = result.unpack("H*")[0] # convert to hexadecimal string
puts seed #=> e1ca8d8539fb054eda16c35dcff74c5f88202b88cb03f2824193f4e6c5e87dd2e24a0edb218901c3e71e900d95e9573d9ffbf870b242e927682e381d109ae882Usage
Where is hashing used in Bitcoin?
Hash functions are a useful general-purpose tool in programming, and they're used liberally throughout Bitcoin.
Here are the most important examples:
Mining
- Relevant Properties: Preimage Resistance, Avalanche Effect
- Hashing Method: HASH256
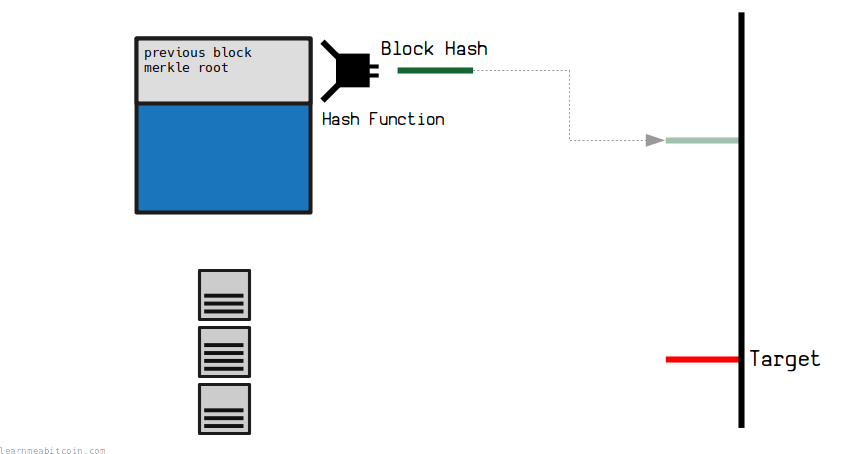
This is the most famous use of the hash function in Bitcoin.
A block header gets hashed, and the resulting block hash is interpreted as an integer. This integer must be below a certain target value for the block to be considered "valid" or "mined".
The fact that the result of the hash function is uncontrollable (preimage resistance) and wildly different for each nonce value (avalanche effect) creates a network-wide lottery, where nobody is in control of when the next block is mined.
Blockchain
- Relevant Properties: Deterministic, Collision Resistance
- Hashing Method: HASH256
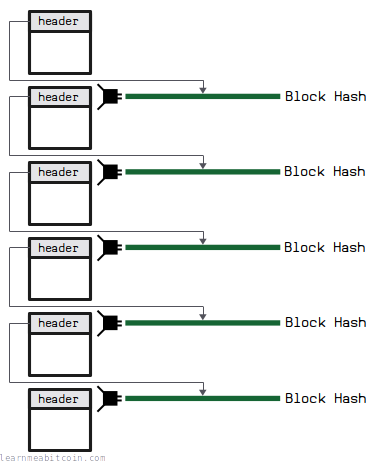
Each block in the blockchain references the hash of previous block. This connects all the blocks in the blockchain together, and prevents anyone from changing the contents of a block anywhere in the chain.
Any change to a block lower down in the chain will change its hash, and therefore the blocks above it will no longer be connected to it and will no longer be part of the longest chain.
TXID
- Relevant Properties: Deterministic, Collision Resistance
- Hashing Method: HASH256
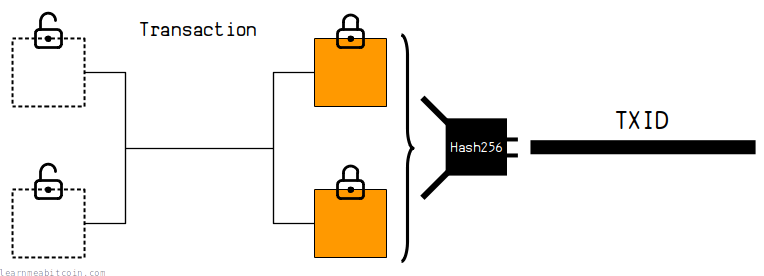
The data for each individual transaction is hashed to create a TXID (Transaction ID). This creates a unique reference number for every transaction (deterministic).
This allows you to reference coins created in previous transactions as inputs for spending in future transactions, as well as being able to search for transactions in a blockchain explorer.
The fact that it's hard to find two pieces of data that hash to the same result (collision resistance) means that every transaction can have its own short and unique reference number.
Merkle Root
- Relevant Properties: Deterministic, Collision Resistance
- Hashing Method: HASH256
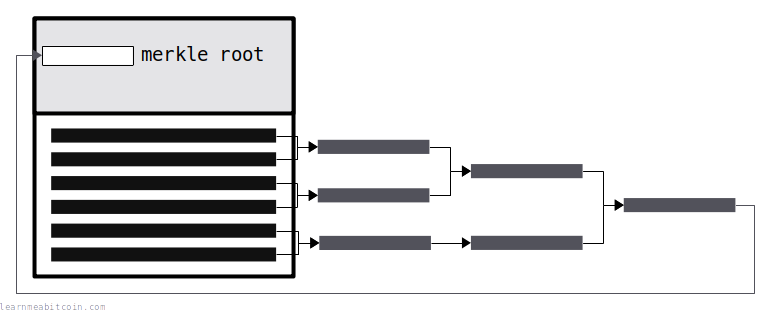
Every block header includes a fingerprint for all of the transaction data included in the block.
This fingerprint is called the merkle root, and it's basically all of the TXIDs hashed together in a tree-like structure.
Hashing allows you to "commit" all the transaction data to the block header (deterministic). Therefore, if anyone changes transaction data in the block, it will no longer match the fingerprint in the header (collision resistance), and the modified block will be invalid.
Checksum
- Relevant Properties: Deterministic, Avalanche Effect
- Hashing Method: HASH256
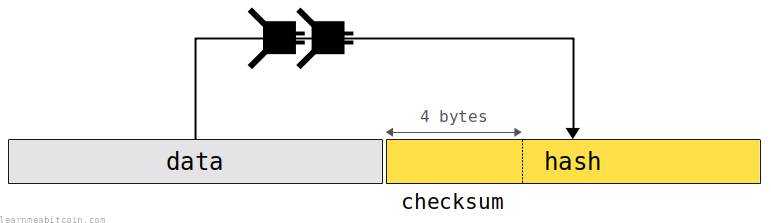
Some checksums are just the truncated hash of some data.
These checksums are bundled with data to allow you to check if the data has been input correctly. For example, a checksum is included at the end of a legacy bitcoin address, so if you type in one part of the address incorrectly, the data will not match the checksum (or vice versa) (avalanche effect), and the error can be detected before you make the transaction.
Checksums are also used in networking to help make sure the contents of a message have not been lost during transit (deterministic).
Public Key Hash
- Relevant Properties: Fixed-Length
- Hashing Method: HASH160
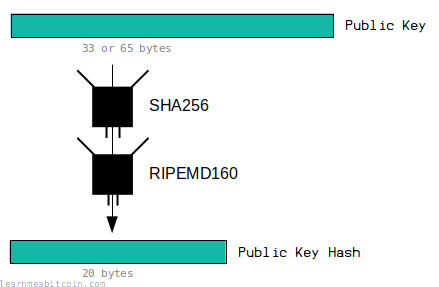
A public key is either 33 or 65 bytes in size. However, before it gets converted to an address, it gets put through a hash function to shorten it to a 20-byte public key hash.
This allows you to create slightly shorter addresses than if you had not hashed the public key beforehand (fixed-length result).
Extended Keys
- Relevant Properties: Preimage Resistance, Collision Resistance
- Hashing Method: HMAC (SHA-512)
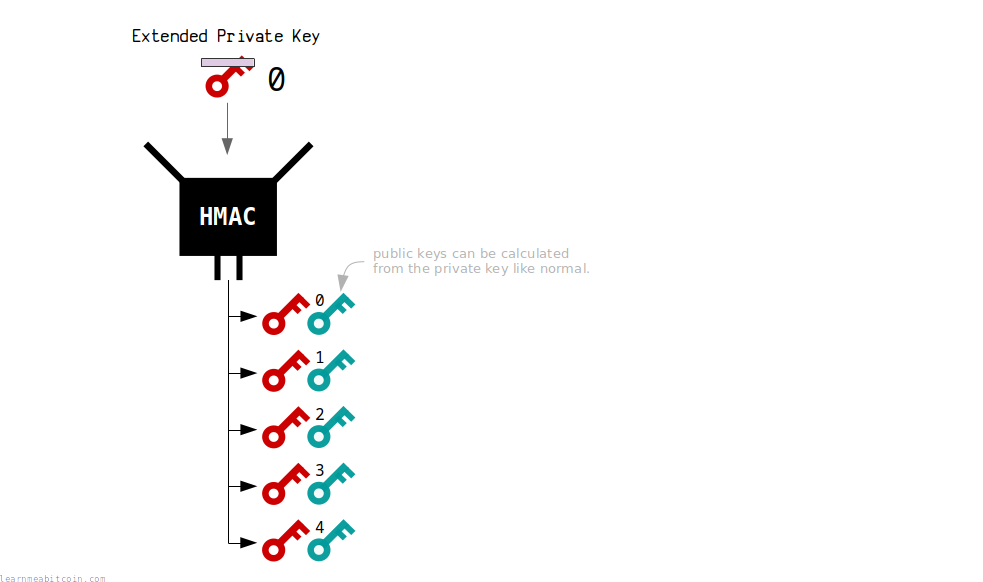
Hierarchical Deterministic Wallets allow you to create multiple private keys from a single seed.
Each extended private key is created by hashing the previous extended private key, which gives you a completely new, unique, and independent private key to use (collision resistance).
This illustrates the security of hash functions, as each new result of the hash function is reliable enough to use as a private key, because you cannot work backwards (preimage resistance) to work out a previous private key from another.
Signing Transactions
- Relevant Properties: Fixed Length, Collision Resistance
- Hashing Method: HASH256
When you sign a transaction, you actually sign a hash of the transaction data.
Hashing data creates a shortened fingerprint for it (fixed-length result), and it's more efficient to sign the hash of a transaction (i.e. 32 bytes) than the full transaction data itself (e.g. 250+ bytes). The hash you sign is also unique for each piece of transaction data (collision resistance), so the resulting signature cannot be reused within a different transaction.
The reason hash functions were invented in the first place was to improve the efficiency of signing long messages.
Notes
How do hash functions work?
Excellent question, I'm glad you asked.
It's at this point I'd usually say that this is "outside the scope of this article" and then distract you with lots of technical terminology and hand waving.
So I made this video on how SHA-256 works instead.
As I say though, a hash function just scrambles and compresses the underlying bits (the 1s and 0s) of computer data. And that's all you really need to know.
A common mistake when hashing
A common mistake when hashing data in Bitcoin is to insert strings into the hash function, and not the underlying byte sequences those strings actually represent.
For example, let's say we have the hexadecimal string ab.
If we insert this directly into the hash function as a string, your programming language will actually send the ASCII encoding of each of these characters into the hash function, which looks like this in binary:
"ab" = 01100001 01100010
sha256(0110000101100010) = fb8e20fc2e4c3f248c60c39bd652f3c1347298bb977b8b4d5903b85055620603
Hash functions work on the underlying 1s and 0s of computer data, which is what I'm referring to here with the word "binary".
But what we actually want to send into the hash function is the byte this hexadecimal string represents, which looks like this in binary:
0xab = 10101011
sha256(10101011) = 087d80f7f182dd44f184aa86ca34488853ebcc04f0c60d5294919a466b463831
This is why we usually need to "pack" our hexadecimal strings in to bytes first before hashing. Most programming languages will have functions that allow you to do this. For example:

 copied
copied copied
copied$hex = "ab"
$binary = pack("H*", $hex);You will probably see a bunch of jargon text if you print out these converted binary values directly. This makes sense, because your programming language converts this binary data back to ASCII when printing it out, and this binary data probably refers to a weird characters (code points) in the ASCII table.
In short, remember that hash functions take in binary data as the input, so we need to be specific about the binary data we want to insert.
If you forget to convert your hexadecimal strings to their corresponding bytes beforehand, your programming language will assume you want to send the binary representation of the characters in the string, and this will produce a completely different hash result than expected.
This is by far the most common issue people have when hashing data in Bitcoin for the first time. So if you're not getting the right hash results, this is probably where you're going wrong.
And I should know, I've done do it myself.
All bitcoin data is just a bunch of bytes at the end of the day. We just use their hexadecimal string representation for convenience when sharing and displaying them on websites.
Summary
A hash function is the Swiss Army knife in the programmer's toolbox.
You'll be hashing things frequently when working with Bitcoin, so it's worth getting the hang of them in whatever programming language you're using.
Satoshi very much understood their properties, and utilized them for various purposes when developing Bitcoin. But their most ingenious decision was to leverage the unpredictability of hash functions to create a network-wide lottery, which is what underpins the revolutionary mechanism of mining and blockchain technology.
So it just goes to show that if you understand the fundamental properties of a tool, you can find new and interesting ways to use it.
Lastly, if you want a proper technical definition of a hash function:
Cryptographic hash functions map input strings of arbitrary (or very large) length to short fixed length output strings.
But I just think of them as fingerprinting machines for data.