copied
copied copied
copied# ---------
# Functions
# ---------
require 'digest'
# hash256 function (checksums use hash256)
def hash256(hex)
binary = [hex].pack("H*")
hash1 = Digest::SHA256.digest(binary)
hash2 = Digest::SHA256.digest(hash1)
result = hash2.unpack("H*")[0]
return result
end
# checksum function
def checksum(hex)
hash = hash256(hex) # Hash the data through SHA256 twice
return hash[0...8] # Return the first 4 bytes (8 characters)
end
# base58 encode function
def base58_encode(hex)
chars = %w[
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
A B C D E F G H J K L M N P Q R S T U V W X Y Z
a b c d e f g h i j k m n o p q r s t u v w x y z
]
base = chars.length
i = hex.to_i(16)
buffer = String.new
while i > 0
remainder = i % base
i = i / base
buffer = chars[remainder] + buffer
end
# add '1's to the start based on number of leading bytes of zeros
leading_zero_bytes = (hex.match(/^([0]+)/) ? $1 : '').size / 2
("1"*leading_zero_bytes) + buffer
end
# ----------
# WIF Encode
# ----------
# 1. start with a 32-byte hexadecimal private key
privatekey = "ef235aacf90d9f4aadd8c92e4b2562e1d9eb97f0df9ba3b508258739cb013db2" # example, do not use
# 2. add prefix (80 = mainet, ef = testnet)
data = "80" + privatekey
# 3. add compression byte (optional)
data = data + "01"
# 4. add checksum
data = data + checksum(data)
# 5. base58 encode
wif = base58_encode(data)
# result
puts wif #=> L5EZftvrYaSudiozVRzTqLcHLNDoVn7H5HSfM9BAN6tMJX8oTWz6
WIF Private Key
Wallet Import Format
A WIF (Wallet Import Format) private key is an address-style format for a private key.
It's used when exporting and importing private keys between bitcoin wallets.
It's mainly a Base58 encoding of the private key, but also includes some extra useful data and a checksum.
A WIF private key is just another way of representing your private key. If you have a WIF private key, you can always convert it back to a raw private key.
Never reveal your WIF private key. A WIF private key is not encrypted in any way, so you need to protect it as much as you would a raw private key.
Benefits
Why do we use WIF private keys?
The main benefit WIF is that it's a Base58 encoding of a private key, so it's shorter and easier to copy.
There are a few other benefits:
- Identification. A WIF private key always starts with a K, L, or 5. This makes them somewhat easier to identify as private keys as opposed to random-looking 32-byte hexadecimal strings. Personally I think this is the most useful benefit of converting a private key to WIF.
- Compression Byte. A WIF private key contains a byte that indicates whether the private key is being used to create a compressed or uncompressed public key. So when you import the WIF private key into a wallet, the wallet can scan the blockchain to look for coins locked to one address, rather than having to scan for a choice of two possible addresses. This is not hugely useful as almost everyone uses compressed public keys anyway, and it wouldn't take too long to scan the blockchain for two types of public keys/addresses, but it's helpful somewhat.
- Checksum. A WIF private key also contains a checksum, which means that you can easily detect if it has been entered incorrectly when importing into a wallet. It's not going to help you fix anything if you've written it down incorrectly in the first place, but it's a minor convenience.
Encoding
Convert a private key to WIF
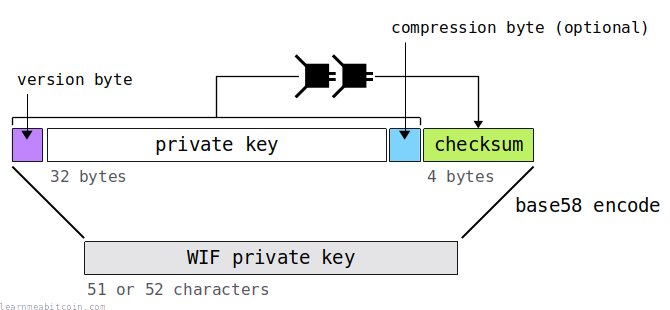
Converting a raw private key to WIF is fairly straightforward:
- Start with a 32-byte hexadecimal private key.
- Add a version byte at the start. This indicates whether the private key is being used on mainnet or testnet:
80= mainnetef= testnet
- Add a compression byte at the end (optional). This indicates whether the private key is being used to create a compressed or uncompressed public key:
01= compressed public key (most common)- (no byte) = uncompressed public key
- Create a checksum from the above data and add it to the end.
- A checksum in Bitcoin is the first 4 bytes of the Hash256 of some data.
- Convert all of the above data to Base58.
And there you have a WIF private key.
For example:
1 byte 32 bytes 1 byte (optional) 4 bytes
version byte private key compression byte checksum
↓ ↓ ↓ ↓
--|--------------------------------------------------------------|--|------|
data = 80ef235aacf90d9f4aadd8c92e4b2562e1d9eb97f0df9ba3b508258739cb013db20166557e53
base58encode(data) = L5EZftvrYaSudiozVRzTqLcHLNDoVn7H5HSfM9BAN6tMJX8oTWz6
Do not use this private key. This is just an example. You will lose your coins if you use it.
Code

 copied
copied copied
copiedimport hashlib # SHA-256 hash function
# 1. start with a 32-byte hexadecimal private key
privatekey = "ef235aacf90d9f4aadd8c92e4b2562e1d9eb97f0df9ba3b508258739cb013db2" # example, do not use
# 2. add prefix (80 = mainet, ef = testnet)
data = "80" + privatekey
# 3. add compression byte (optional)
data = data + "01"
# 4. add checksum (hash256 the prefix+data+checksum, then take the first 4 bytes)
hash1 = hashlib.sha256(bytes.fromhex(data)).digest() # convert hex string to raw bytes before hashing
hash2 = hashlib.sha256(hash1).hexdigest() # return result as hex string
checksum = hash2[0:8] # checksum is the first 4 bytes
data = data + checksum # add checksum to the end of the data
# 5. set base58 characters
characters = ['1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9', 'A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E', 'F', 'G', 'H', 'J', 'K', 'L', 'M', 'N', 'P', 'Q', 'R', 'S', 'T', 'U', 'V', 'W', 'X', 'Y', 'Z', 'a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 'f', 'g', 'h', 'i', 'j', 'k', 'm', 'n', 'o', 'p', 'q', 'r', 's', 't', 'u', 'v', 'w', 'x', 'y', 'z']
# 6. convert hex data to integer so we can convert it to base58
i = int(data, 16)
# 7. create a buffer for holding the base58 string
base58 = ''
# 8. keep dividing the integer by 58 and taking the remainder to work out each base58 character
while i > 0:
i, remainder = divmod(i, 58) # divide and get the remainder
base58 = characters[remainder] + base58 # use the remainder to get the character, and add it to the start of the string
# note: during normal base58 encoding you convert leading 00 bytes in hex to 1s in base58, but leading zero bytes will not be present when creating a wif private key so we're skipping that step here
# 9. show result (wif private key)
print(base58) #=> L5EZftvrYaSudiozVRzTqLcHLNDoVn7H5HSfM9BAN6tMJX8oTWz6
- On mainnet, a WIF should start with a K, L, or 5.
- On testnet, a WIF should start with a c or a 9.
Decoding
Convert from WIF to a private key
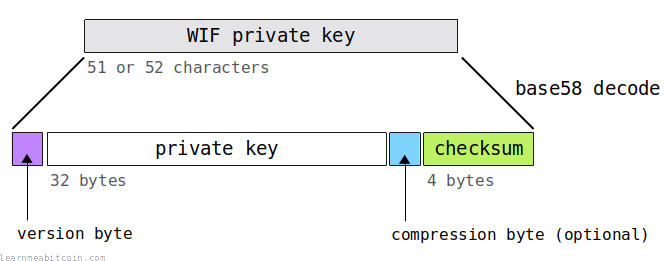
It's easy enough to extract a raw private key from WIF:
- Start with the 51 or 52 character WIF private key.
- Decode it from Base58.
- This will give you 37 or 38 hexadecimal bytes.
- The private key is contained within bytes 1-33 (i.e. ignore the first 2 characters, then take the next 64 characters).
For example:
address = L5EZftvrYaSudiozVRzTqLcHLNDoVn7H5HSfM9BAN6tMJX8oTWz6
base58decode(address) = 80ef235aacf90d9f4aadd8c92e4b2562e1d9eb97f0df9ba3b508258739cb013db20166557e53
--|--------------------------------------------------------------|--|------|
↑ ↑ ↑ ↑
version byte private key compression byte checksum
1 byte 32 bytes 1 byte (optional) 4 bytes
Do not use this private key. This is just an example. You will lose your coins if you use it.
You can also extract additional data from the WIF private key (if you need to):
- The first byte is the version byte, which is used to determine if the private key is meant to be used on mainnet or testnet.
80= mainnetef= testnet
- The optional byte after the private key is the compression byte, which is used to determine if the private key was used to create a compressed or uncompressed public key. If it's not there (i.e. you've only got 37 bytes after decoding from Base58), then it indicates an uncompressed public key.
01= compressed public key (most common)- (no byte) = uncompressed public key
- The last 4 bytes are the checksum, which allows you to check if the WIF is valid or not
Code

 copied
copied copied
copied# ---------
# Functions
# ---------
# base58 decode function
def base58_decode(base58_string)
# base58 characters
base58_chars = "123456789ABCDEFGHJKLMNPQRSTUVWXYZabcdefghijkmnopqrstuvwxyz"
# set starting integer value
integer = 0
# run through each character in the string from right to left
base58_string.reverse.each_char.with_index do |char, index|
# get the position of the character in the list of base58 characters
char_index = base58_chars.index(char)
# check its a valid base58 character
if !char_index
puts "Not a valid Base58 character: #{char}"
exit
end
# multiply the position of the character by a power of 58 (increasing for the index of each character)
integer += char_index * (58**index)
end
# convert the integer to a hexadecimal string
hexadecimal = integer.to_s(16)
# pad out to make sure it's an even number of bytes
if hexadecimal.bytesize.odd?
hexdecimal = "0" + hexadecimal
end
# ignore empty base58 strings
if hexadecimal == "00"
hexadecimal = ""
end
# count the number of leading 1's
leading_zero_bytes = (base58_string.match(/^([1]+)/) ? $1 : '').size
# convert leading 1's to leading 00's
if leading_zero_bytes > 0
hexadecimal = ("00" * leading_zero_bytes) + hexadecimal
end
# return hexadecimal bytes
return hexadecimal
end
# ----------
# WIF Decode
# ----------
# 1. start with a wif private key
wif = "L5EZftvrYaSudiozVRzTqLcHLNDoVn7H5HSfM9BAN6tMJX8oTWz6" # example, do not use
# 2. base58 decode
data = base58_decode(wif)
# 3. extract the private key (bytes 1 to 33)
privatekey = data[2...66]
# result
puts privatekey #=> ef235aacf90d9f4aadd8c92e4b2562e1d9eb97f0df9ba3b508258739cb013db2

 copied
copied copied
copied# 1. start with a wif private key
wif = "L5EZftvrYaSudiozVRzTqLcHLNDoVn7H5HSfM9BAN6tMJX8oTWz6" # example, do not use
# 2. set base58 characters
characters = ['1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9', 'A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E', 'F', 'G', 'H', 'J', 'K', 'L', 'M', 'N', 'P', 'Q', 'R', 'S', 'T', 'U', 'V', 'W', 'X', 'Y', 'Z', 'a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 'f', 'g', 'h', 'i', 'j', 'k', 'm', 'n', 'o', 'p', 'q', 'r', 's', 't', 'u', 'v', 'w', 'x', 'y', 'z']
# 3. convert base58 string to integer
# 3a. reverse the base58 string so we can work from right to left
wif = wif[::-1]
# 3b. set starting value
sum = 0
# 3c. run through each character in the wif private key (the base58 string)
for i, c in enumerate(wif):
# 3d. get the index number of this character from the list of base58 characters
for index, base58_character in enumerate(characters): # this is a basic way to find the key from the list, but it works
if (c == base58_character):
character_index = index
break # stop looking
# 3e. multiply the index of the character by a power of 58 (increasing the power based on the position of the character in the base58 string), then add this to the sum
sum += character_index * (58**i)
# 4. convert integer to a hexadecimal
hexadecimal = hex(sum)[2:] # remove the 0x prefix using [2:]
# note: during normal base58 decoding you convert leading 1s in base58 to leading 00 bytes in hex, but wif private keys never start with a 1 so we're skipping that step here
# 5. extract the private key (ignore the prefix, compression byte, and checksum)
privatekey = hexadecimal[2:66]
# 6. pad out the private key so it always shows as 32 bytes (64 hexadecimal characters)
privatekey = privatekey.zfill(64) # zfill pads with zeros at the start to the desired length
# 6. show result
print(privatekey) #=> ef235aacf90d9f4aadd8c92e4b2562e1d9eb97f0df9ba3b508258739cb013db2
Usage
Where are WIF private keys used in Bitcoin?
As mentioned, WIF is used when you're exporting or importing private keys between wallets.
Some examples of popular wallets that use WIF are:
From my experience it's more common for wallets to require you to work with WIF private keys as opposed to allowing you to import/export raw private keys.
History
When were WIF private keys introduced in Bitcoin?
Pieter Wuille created the WIF format in 2011 for importing and exporting private keys via Bitcoin Core.
https://github.com/bitcoin/bitcoin/pull/574
Thanks to Murch and Ava Chow for the help with the origin of WIF private keys.
Summary
WIF is just designed to be a more user-friendly encoding of a private key.
You can spot a WIF private key because it's a Base58 string and starts with a K or L. On the odd occasion it will start with a 5 (if you're working with uncompressed public keys for some reason). For example:
These are static examples of WIF private keys. Do not use them.
- Ky1BY5QkB6xb3iQQjJQmVcvqc6mkLBaZTW1xCWpf91aFGBh1kyQ7 (for a compressed public key on mainnet)
- L1Rw26ZuhBqguYDSi77zAxyfHUZ2H1JAQunf3TEbxyfcBDjUvBse (for a compressed public key on mainnet)
- 5JKZUnxc5G8toCqErCQpHiUYff3t7GvBd2my4bf6odejtZAy7hG (for an uncompressed public key on mainnet)
So if you're working on mainnet with compressed public keys like a normal person, look for the K or L at the start.
From my experience it can be a bit annoying to have to convert between raw private key and WIF when you want to import a private key into a wallet, but it's common practice for wallets to work with WIF instead of raw private keys, so you might as well get used to it.
If you're working with raw private keys locally (and occasionally want to import/export them), it's a good idea to write your own WIF encoder/decoder. The last thing you want to do is trust a website or tool to handle your private keys, and it's not hard to create a tool that converts between WIF and a raw private key yourself.
It will save time and stress later on. Trust me.
Because as that famous old saying goes, "Not Your Own WIF Tool, Not Your Coins".
Or something like that.
Resources
Tools
- WIF Decode, WIF Encode — Handy command-line tools for converting between a hex private key and WIF on your local computer.